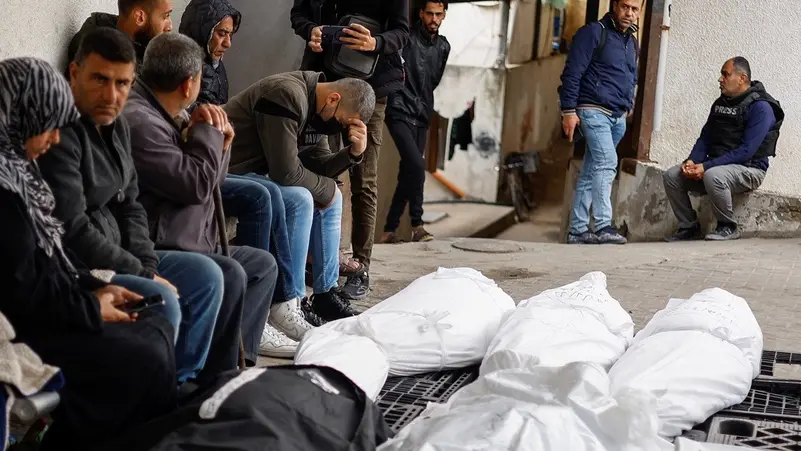
The ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas, which has roots in decades of geopolitical and ideological tensions, has escalated significantly in recent months. Below is a brief history of the conflict leading up to the recent violence and developments.
The Israel-Palestine conflict, which spans over a century, traces its origins to the late 19th and early 20th centuries with competing national movements among Jews and Arabs. Following the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, wars and territorial disputes ensued. The Gaza Strip, where Hamas is based, was originally under Egyptian control but was occupied by Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. Since then, the region has remained a major focal point of contention.
Hamas’s Rise to Power:
Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist militant group, was founded in 1987 during the First Intifada (Palestinian uprising) as an offshoot of the Egyptian Muslim Brotherhood. Hamas’s goal is to establish an Islamic state in all of historic Palestine, including what is now Israel. The group’s use of violence, including suicide bombings and rocket attacks, against Israel has made it a significant player in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
In 2006, Hamas won the Palestinian legislative elections and subsequently took control of the Gaza Strip in 2007 after a violent struggle with the rival Palestinian faction Fatah. Since then, Hamas has governed Gaza, while the Palestinian Authority, dominated by Fatah, controls the West Bank. Israel and many Western countries, including the U.S. and EU, classify Hamas as a terrorist organization due to its attacks on Israeli civilians.
Recent Escalation (October 2023):
The latest wave of violence began on October 7, 2023, when Hamas launched a large-scale attack on Israel. This surprise assault included rocket fire and the infiltration of armed militants into Israel. The attack killed around 1,200 Israelis, most of them civilians, and resulted in the kidnapping of 251 hostages, including women, children, and elderly individuals.
In response, Israel launched Operation Iron Swords, a massive military operation aimed at dismantling Hamas’s military infrastructure and securing the release of hostages. Israel’s strikes in Gaza targeted Hamas military sites, tunnels, and leadership. Over 48,500 Palestinians, mostly civilians, were killed in Israel’s response, and tens of thousands were displaced as Gaza’s infrastructure was decimated.
Ceasefire and Renewed Violence:
A brief ceasefire was brokered in January 2024, with both sides agreeing to halt large-scale military operations. However, this peace was short-lived. Negotiations to extend the ceasefire failed in March 2025, prompting Israel to renew its offensive on March 18, 2025.
Current Developments (March 2025):
On March 21, 2025, Hamas launched three rockets at Tel Aviv, marking the first retaliatory missile strike since Israel resumed its offensive. The IDF intercepted one missile, while the others landed in uninhabited areas. Israel’s military responded by continuing its ground operations, focusing on dismantling Hamas’s infrastructure in the Gaza Strip. The IDF deployed troops in Rafah, near the Egyptian border, and expanded operations in central and northern Gaza.
Since the resumption of fighting, at least 591 people have died in Gaza, including more than 200 children. Israel’s government has blamed Hamas for the escalation, citing its refusal to release hostages and its rejection of multiple ceasefire offers mediated by the U.S. and other countries.
Humanitarian Impact:
The violence has had a devastating impact on civilians. Hospitals in Gaza are overwhelmed with casualties, and many medical staff members have been killed in the ongoing airstrikes. The UN has reported the deaths of five of its workers, and the destruction of medical and humanitarian infrastructure has worsened the already dire conditions for residents.
International organizations have warned of a humanitarian crisis in Gaza, with food, medical supplies, and fuel running low. Israel has imposed a blockade on Gaza, which it accuses Hamas of using to fuel its military efforts. Meanwhile, international calls for a ceasefire have been met with resistance from both sides.
International Reactions:
Israel’s actions are largely supported by the United States, which has long been a key ally of Israel. However, several European countries and the United Nations have called for restraint, urging both sides to seek peace. The U.S. has reaffirmed its support for Israel’s right to defend itself while also emphasizing the importance of adhering to international law in the conduct of military operations.
Hamas and Hostages:
As of March 2025, Israel continues to demand the release of the remaining 59 hostages held by Hamas, including 24 believed to still be alive. The ongoing negotiations over hostages have failed, with Hamas offering to release some hostages, but Israel insists that all must be freed. Some hostages’ families have criticized Israel’s decision to resume military operations, claiming it jeopardizes the lives of their loved ones.
The conflict continues to draw international attention, with neighboring countries like Lebanon, Syria, and Egypt involved in diplomatic efforts. The conflict has also attracted involvement from proxy groups such as Yemen’s Houthi rebels, who launched a ballistic missile at Israel in March 2025, which was intercepted before causing any damage.
Conclusion:
The Israel-Hamas conflict remains one of the most entrenched and complex geopolitical disputes in the world. Despite various ceasefires and international efforts to mediate peace, both sides continue to pursue military solutions. As the situation evolves, the humanitarian toll and the prospects for peace remain uncertain, with the world watching closely for signs of a resolution.